Mastering Solar Energy: What You Need to Know & How It Works is a comprehensive guide that explores the inner workings of solar energy and its role in creating a sustainable future, empowering readers with the knowledge to harness clean and affordable renewable energy.

Mastering Solar Energy: Which is Right for You DIY or Commercial ?
Harnessing solar energy can reduce your carbon footprint and save on electricity, but it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of both options. Your decision will impact your energy independence, costs, and long-term satisfaction.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics, compare DIY and commercial solar, and help you find the best fit for your needs. Ready to start your solar journey? Let’s dive in!
1. Understanding Solar Energy Basics
As you explore solar power options, it’s important to understand the basics of this clean energy. In this section, we’ll explain how solar panels work, highlight the benefits, and outline the key components of a solar power system—providing a foundation for choosing between DIY and commercial solutions.
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels are the cornerstone of any solar power system, converting sunlight into usable electricity for your home or business. To truly appreciate the value of solar energy, you need to understand the science behind these remarkable devices.
The Photovoltaic Effect
At the heart of solar panel technology lies the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon occurs when certain materials, primarily silicon, generate an electric current when exposed to light. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Sunlight strikes the solar panel’s surface.
- Photons (particles of light) interact with the silicon atoms in the panel.
- This interaction causes electrons to be knocked loose from their atoms.
- The freed electrons flow through the material, creating an electric current.
- This current is then captured and converted into usable electricity for your home.
Solar Cell Construction
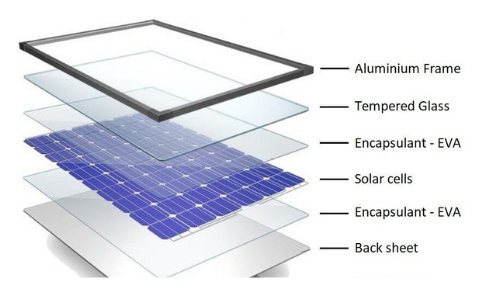
To harness the photovoltaic effect effectively, solar panels are composed of multiple layers:
- Protective Glass: A durable, anti-reflective glass covers the top of the panel to shield the internal components from the elements while allowing maximum light penetration.
- Encapsulant Layer: This thin layer of polymer protects the silicon cells from moisture and contaminants.
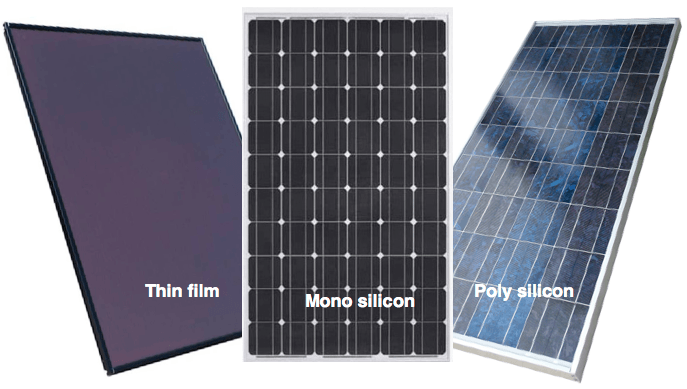
- Silicon Cells: The heart of the solar panel, these cells are typically made of either monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon. Monocrystalline cells are more efficient but also more expensive, while polycrystalline cells offer a balance between cost and performance.
- Back Sheet: A protective layer on the bottom of the panel that provides electrical insulation and moisture resistance.
- Frame: An aluminum frame surrounds the entire panel, providing structural support and easy mounting options.
Efficiency and Power Output
The efficiency of your solar panels plays a crucial role in determining how much power you can generate. Here are some key factors that affect solar panel efficiency:
- Cell Type: Monocrystalline cells are generally more efficient than polycrystalline cells.
- Panel Orientation: Panels facing directly towards the sun produce more power.
- Temperature: Solar panels actually perform better in cooler temperatures, as excessive heat can reduce efficiency.
- Shading: Even partial shading can significantly reduce a panel’s output.
- Age: Solar panels gradually lose efficiency over time, typically at a rate of 0.5-1% per year.
To give you a better understanding of how these factors translate into real-world performance, here’s a comparison of typical power outputs for different types of solar panels:
| Panel Type | Efficiency Range | Typical Power Output (300W panel) |
| Monocrystalline | 17-22% | 250-270W |
| Polycrystalline | 15-17% | 230-250W |
| Thin-Film | 10-13% | 180-220W |
Remember, these figures are general estimates, and actual performance can vary based on specific models and environmental conditions.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Now that you understand how solar panels work, let’s explore the numerous advantages that make solar energy an attractive option for homeowners and businesses alike.
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By generating clean electricity, you significantly decrease your reliance on fossil fuels and lower your carbon emissions.
- Minimal Water Usage: Unlike traditional power plants, solar panels require very little water to operate, helping conserve this precious resource.
- Noise-Free Operation: Solar panels generate electricity silently, contributing to a more peaceful environment.
- Land Conservation: Rooftop solar installations don’t require additional land use, preserving natural habitats and agricultural areas.
Economic Advantages
- Lower Electricity Bills: By generating your own power, you can substantially reduce or even eliminate your monthly electricity costs.
- Protection Against Rising Energy Prices: As utility rates continue to climb, your solar system provides a hedge against future price increases.
- Increased Property Value: Homes with solar installations often sell for a premium compared to those without.
- Tax Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer financial incentives to encourage solar adoption, further reducing your overall costs.
Energy Independence
- Reduced Reliance on the Grid: With a properly sized system, you can significantly decrease your dependence on the utility grid.
- Potential for Off-Grid Living: When combined with battery storage, solar power can enable complete energy independence in remote locations.
- Energy Security: Solar power provides a reliable source of electricity during grid outages or natural disasters.
Long-Term Reliability
- Durability: Most solar panels come with 25-30 year warranties and can last even longer with proper maintenance.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: Solar systems have few moving parts, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
- Consistent Performance: Solar panels maintain their efficiency well over time, with only minimal degradation (typically 0.5-1% per year).
To illustrate the long-term benefits of solar energy, consider this comparison of cumulative energy savings over a 25-year period:
| Year | Cumulative Energy Savings (kWh) | Estimated Cost Savings ($) |
| 5 | 30,000 | $3,600 |
| 10 | 60,000 | $7,200 |
| 15 | 90,000 | $10,800 |
| 20 | 120,000 | $14,400 |
| 25 | 150,000 | $18,000 |
Note: This example assumes a 5kW system in a sunny location with an average electricity rate of $0.12/kWh. Actual savings may vary based on your specific circumstances.
Components of a Solar Power System
To fully appreciate the complexity and functionality of solar power, it’s essential to understand the various components that work together to harness the sun’s energy and power your home or business. Let’s break down the key elements of a typical solar power system:
1. Solar Panels
As we’ve discussed earlier, solar panels are the primary component of any solar power system. They’re responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into direct current (DC) electricity. When designing your system, you’ll need to consider:
- Number of Panels: This depends on your energy needs and available space. Read more for Solar Panel Sizing
- Panel Efficiency: Higher efficiency panels produce more power in less space but may cost more.
- Panel Orientation: Ideally, panels should face south in the Northern Hemisphere for maximum sun exposure.

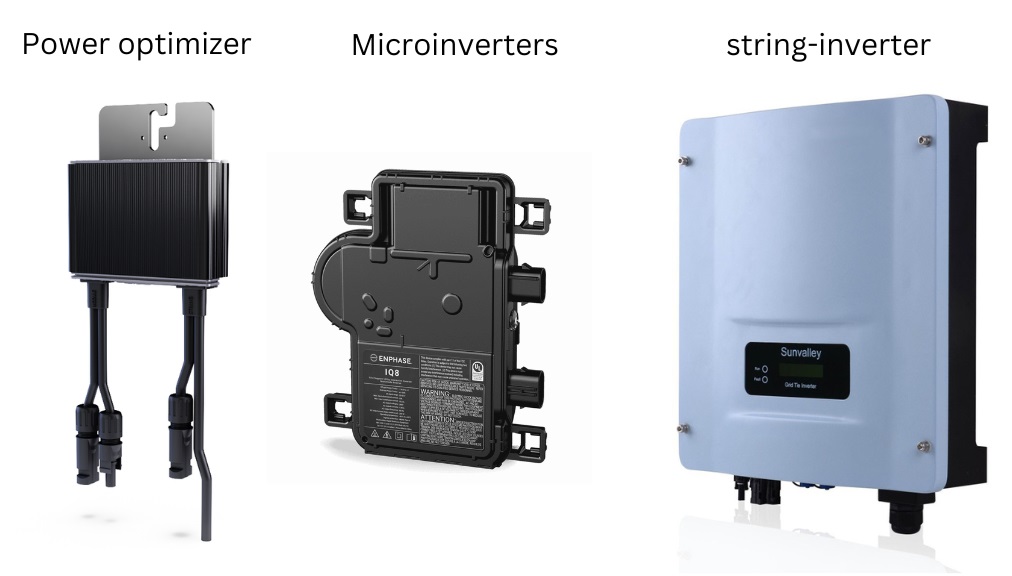
2. Inverter
The inverter is a crucial component that converts the DC electricity produced by your solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by most household appliances and the power grid. There are three main types of inverters:
- String Inverters: These are the most common and cost-effective option, connecting multiple panels in a series.
- Microinverters: Attached to each individual panel, these allow for panel-level monitoring and optimization but are more expensive.
- Power Optimizers: A hybrid solution that combines string inverters with panel-level optimization.

3. Mounting System
The mounting system secures your solar panels to your roof or ground-mounted structure. Key considerations include:
- Roof Type: Different roofing materials require specific mounting solutions.
- Tilt Angle: The optimal tilt angle depends on your latitude and local climate.
- Wind and Snow Load: Your mounting system must be able to withstand local weather conditions.
4. Electrical Wiring and Conduit
Proper wiring is essential for safely transmitting electricity from your panels to your inverter and then to your home’s electrical system. This includes:
- DC Wiring: Connects solar panels to the inverter.
- AC Wiring: Carries inverted AC electricity to your home’s electrical panel.
- Conduit: Protects wiring from the elements and meets local building codes.
5. Monitoring System
A monitoring system allows you to track your solar power production and consumption in real-time. Features often include:
- Energy Production Data: View daily, monthly, and annual power generation.
- Performance Alerts: Receive notifications about system issues or underperformance.
- Mobile App Integration: Access your system data from anywhere via smartphone.
6. Electrical Meter
Your existing electrical meter will typically be replaced with a bi-directional meter that can measure both the electricity you draw from the grid and the excess power your system sends back to it.
7. Battery Storage (Optional)
While not essential, battery storage systems are becoming increasingly popular. They allow you to:
- Store excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days.
- Provide backup power during grid outages.
- Maximize self-consumption of your solar-generated electricity.
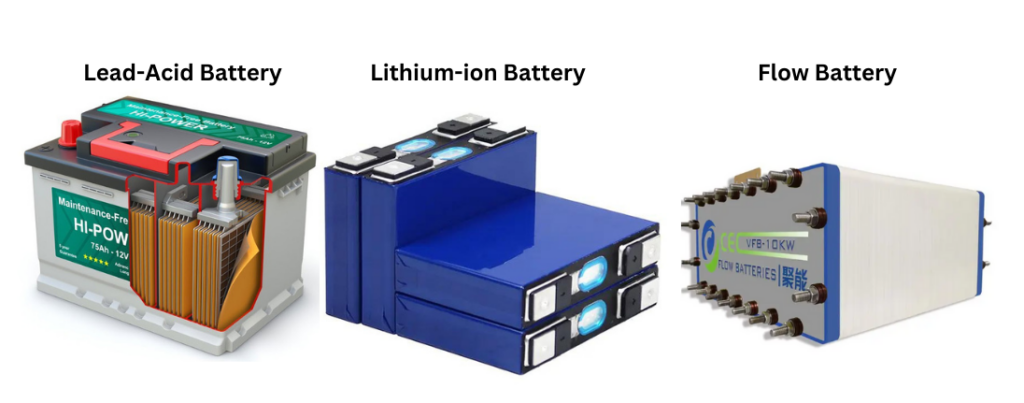
Popular battery options include:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: High efficiency and long lifespan, but more expensive.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: More affordable but require more maintenance and have a shorter lifespan.

8. Charge Controller (for Off-Grid Systems)
If you’re considering an off-grid system with battery storage, you’ll need a charge controller to:
- Regulate the voltage and current from the solar panels to the batteries.
- Prevent overcharging and extend battery life.
9. Disconnects and Circuit Breakers
Safety components are crucial in any solar power system. These include:
- DC Disconnect: Allows you to safely shut off the flow of electricity from your solar panels.
- AC Disconnect: Enables you to disconnect your system from the grid when necessary.
- Circuit Breakers: Protect your system and home from electrical surges.
To help you visualize how these components work together, here’s a simplified diagram of a typical Off-grid solar energy system:
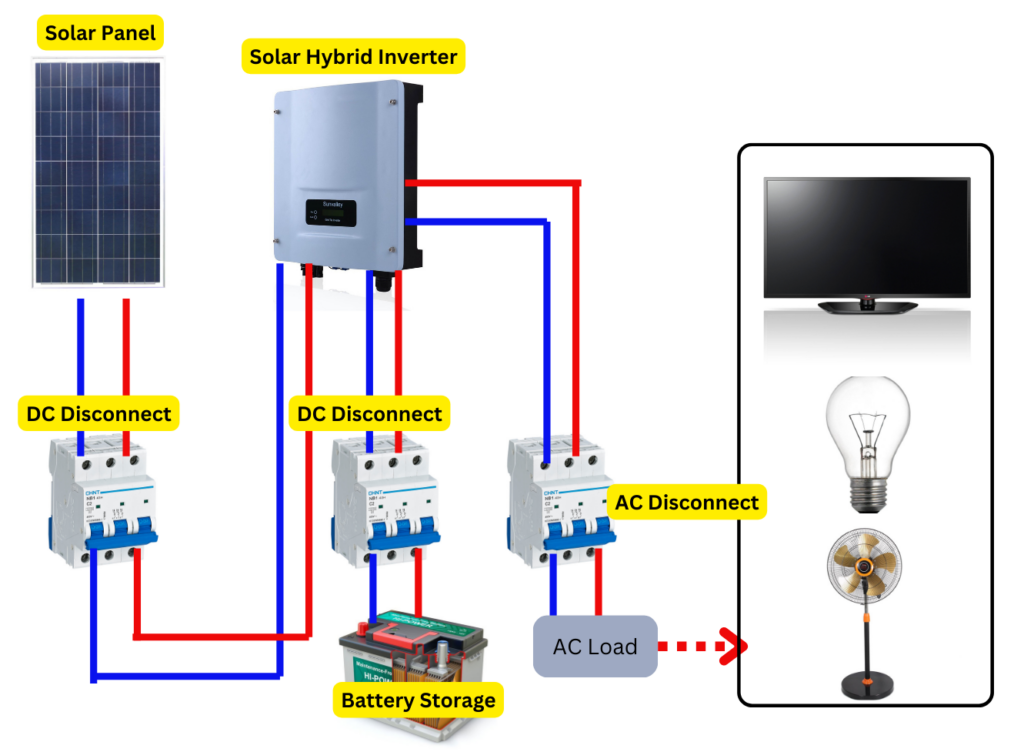
Understanding these components and their functions is crucial when deciding between a DIY and commercial solar installation. A DIY approach requires you to select, source, and install each of these elements correctly, while a commercial installation typically handles this complexity for you.
As we move forward, you’ll see how this foundational knowledge of solar power basics will inform your decision-making process. Whether you choose to tackle a DIY installation or opt for a professional commercial solution, your understanding of these core concepts will help you make the most of your solar investment.
Now that you have mastering solar energy fundamentals, let’s explore the pros and cons of DIY solar power installations in the next section. This comparison will help you weigh the benefits and challenges of taking on a solar project yourself versus opting for a commercial solution.
DIY Solar Power: Pros and Cons
Now that you understand the basics of solar power, let’s explore the world of DIY solar installations. This approach to harnessing solar energy has gained popularity among homeowners looking to take a more hands-on approach to renewable energy. But is it the right choice for you? Let’s dive into the pros and cons of DIY solar power to help you make an informed decision.
A. Potential risks and challenges
While the idea of installing your own solar system can be exciting, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and challenges you might face along the way. Here are some key considerations:
- Safety concerns: Working with electrical systems and on rooftops can be dangerous. You’ll need to take proper safety precautions to avoid accidents and injuries.
- Permit and code compliance: Navigating local building codes and obtaining necessary permits can be complex and time-consuming for DIY installers.
- Design and sizing errors: Without professional expertise, you might make mistakes in system design or sizing, leading to suboptimal performance or even system failure.
- Equipment selection: Choosing the right components and ensuring their compatibility can be challenging for those new to solar technology.
- Warranty issues: Some manufacturers may void warranties if their products are not installed by certified professionals.
- Grid connection: Connecting your system to the grid requires coordination with your local utility company, which can be complicated for DIY installers.
- Roof damage: Improper installation techniques could lead to roof leaks or structural damage.
- Performance optimization: Achieving maximum efficiency from your solar system requires expertise in positioning and configuration.
To illustrate these challenges, consider the following comparison table:
| Challenge | DIY Solar | Professional Installation |
| Safety | Higher risk due to lack of experience | Lower risk with trained professionals |
| Code compliance | Complex for homeowners to navigate | Handled by experienced installers |
| System design | Potential for errors | Optimized by experts |
| Equipment selection | Limited knowledge of options | Access to latest technology |
| Warranty coverage | May be voided | Typically fully covered |
| Grid connection | Can be complicated | Managed by professionals |
| Roof integrity | Higher risk of damage | Minimal risk with proper techniques |
| Performance | May be suboptimal | Optimized for maximum efficiency |
Despite these challenges, many homeowners successfully complete DIY solar installations. However, it’s crucial to honestly assess your skills, time, and resources before embarking on this journey.
B. Personal satisfaction and learning experience
One of the most significant advantages of a DIY solar installation is the personal satisfaction and learning experience it provides. Here’s why many homeowners find this aspect appealing:
- Hands-on learning: You’ll gain in-depth knowledge about solar technology, electrical systems, and renewable energy.
- Skill development: Installing your own system helps you develop valuable technical and problem-solving skills.
- Sense of accomplishment: Successfully completing a DIY solar project can be incredibly rewarding and boost your confidence.
- Greater system understanding: By installing the system yourself, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how it works, which can be helpful for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Environmental impact awareness: The process of installing your own solar system can increase your awareness of energy consumption and environmental issues.
- Community engagement: DIY solar projects often lead to connections with like-minded individuals and can inspire others in your community to explore renewable energy options.
- Customization experience: You’ll learn about various solar components and how to tailor a system to your specific needs.
- Problem-solving skills: Overcoming challenges during the installation process can enhance your ability to tackle complex problems.
To make the most of this learning experience, consider the following tips:
- Research thoroughly before starting your project
- Join online forums or local groups focused on DIY solar installations
- Document your progress and share your experiences with others
- Attend workshops or webinars on solar technology and installation techniques
- Consult with experienced DIY solar installers for advice and guidance
Remember that while the learning experience can be valuable, it’s essential to balance this with the potential risks and challenges mentioned earlier.
C. Customization options
One of the most appealing aspects of DIY solar power is the level of customization it offers. When you take on a DIY solar project, you have greater control over various aspects of your system. Here’s how you can customize your solar installation:
- System size: You can tailor the size of your solar array to match your specific energy needs and available space.
- Panel selection: Choose from a wide range of solar panels based on efficiency, aesthetics, and budget.
- Inverter type: Decide between string inverters, microinverters, or power optimizers based on your system design and shading conditions.
- Mounting system: Select the most suitable mounting option for your roof type or opt for a ground-mounted system.
- Battery storage: Incorporate battery storage solutions to increase energy independence and provide backup power.
- Smart home integration: Integrate your solar system with home automation devices for enhanced energy management.
- Expandability: Design your system with future expansion in mind, allowing for easy addition of panels or batteries.
- Aesthetics: Choose panel layouts and colors that complement your home’s architectural style.
To help you understand the customization options available, consider the following table:
| Customization Area | Options |
| System Size | 1-5 kW (small), 5-10 kW (medium), 10+ kW (large) |
| Panel Types | Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, Thin-film |
| Inverter Types | String inverters, Microinverters, Power optimizers |
| Mounting Systems | Roof-mounted, Ground-mounted, Tracking systems |
| Battery Storage | Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, Flow batteries |
| Smart Home Integration | Energy monitoring systems, Smart thermostats, Home energy management systems |
| Expandability | Oversized inverters, Additional roof space, Pre-wiring for future panels |
| Aesthetic Options | Black-on-black panels, In-roof systems, Solar tiles |
When customizing your DIY solar system, keep these factors in mind:
- Energy needs: Analyze your current and future energy consumption to determine the appropriate system size.
- Roof characteristics: Consider your roof’s orientation, angle, and available space when designing your system.
- Local climate: Choose components that perform well in your specific climate conditions.
- Budget constraints: Balance your desire for high-end components with your budget limitations.
- Future plans: Consider potential changes in your energy needs or home improvements that might affect your solar system.
By carefully considering these customization options, you can create a solar power system that perfectly meets your needs and preferences. However, it’s important to note that with greater customization comes increased complexity in design and installation. Ensure you have the necessary knowledge and skills to implement your chosen customizations effectively.
D. Cost savings potential
One of the primary motivations for choosing a DIY solar installation is the potential for significant cost savings. By taking on the project yourself, you can reduce or eliminate labor costs, which typically account for a substantial portion of the total system price. Let’s explore the cost savings potential of DIY solar power:
- Labor cost elimination: By installing the system yourself, you can save on professional installation fees, which can range from $5,000 to $15,000 or more, depending on the system size and complexity.
- Equipment cost savings: DIY installers often have more flexibility in sourcing equipment, potentially finding better deals on panels, inverters, and other components.
- No markup on materials: Professional installers often add a markup to equipment costs, which you can avoid by purchasing directly from suppliers or manufacturers.
- Tax credits and incentives: DIY installations are still eligible for federal tax credits and many state and local incentives, further reducing your overall costs.
- Gradual investment: You can build your system incrementally, spreading the cost over time as your budget allows.
- Long-term energy savings: Regardless of the installation method, a solar power system will reduce or eliminate your electricity bills over its lifetime.
- Increased home value: Solar installations typically increase property values, providing a return on your investment if you decide to sell your home.
- Potential for oversizing: DIY installers may choose to oversize their systems to maximize long-term savings, an option that might be cost-prohibitive with professional installation.
To illustrate the potential cost savings, let’s compare the costs of a DIY installation versus a professional installation for a typical 5kW residential solar system:
| Cost Category | DIY Installation | Professional Installation |
| Equipment | $7,500 – $10,000 | $9,000 – $12,000 |
| Labor | $0 (your time) | $5,000 – $7,000 |
| Permits and Inspections | $500 – $1,000 | Included in labor costs |
| Additional Tools/Equipment | $500 – $1,000 | Not applicable |
| Total Cost | $8,500 – $12,000 | $14,000 – $19,000 |
| Potential Savings | $5,500 – $7,000 | Baseline |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on location, system specifics, and market conditions.
While the cost savings potential of DIY solar is significant, it’s crucial to consider the following factors:
- Value of your time: Calculate the hours you’ll spend on research, planning, and installation, and consider the opportunity cost.
- Quality of work: Ensure that your installation quality matches professional standards to maximize system efficiency and longevity.
- Potential for mistakes: Factor in the cost of potential errors or rework that might be necessary if issues arise.
- Maintenance and repairs: Consider long-term costs associated with maintaining and repairing the system yourself.
- Insurance implications: Check if your homeowner’s insurance covers DIY solar installations or if additional coverage is needed.
To maximize your cost savings:
- Research thoroughly to find the best equipment deals without compromising on quality.
- Take advantage of bulk purchasing options for solar panels and other components.
- Coordinate with other DIY solar installers in your area to share tools or bulk-order materials.
- Stay informed about available tax credits, rebates, and incentives in your area.
- Consider joining a solar co-op or group purchase program to leverage collective buying power.
While DIY solar installations can offer significant cost savings, it’s essential to weigh these savings against the potential risks, time investment, and long-term implications. Carefully assess your skills, resources, and willingness to take on the responsibility of a DIY installation before making your decision.
As we’ve explored the pros and cons of DIY solar power, including the potential risks and challenges, personal satisfaction and learning experience, customization options, and cost savings potential, you now have a comprehensive understanding of what a DIY solar installation entails. Next, we’ll examine the advantages and disadvantages of commercial solar power to provide a balanced comparison and help you make the best choice for your specific situation.
Commercial Solar Power: Advantages and Disadvantages
Now that you’re familiar with DIY solar power options, let’s explore the world of commercial solar power. This approach involves purchasing a solar system from a professional company that handles everything from design to installation. While it may seem less hands-on than the DIY route, commercial solar power comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Let’s dive into the details to help you determine if this option aligns with your energy goals.
A. Limited customization options
When you opt for commercial solar power, you’ll find that customization options are often more limited compared to DIY solutions. This aspect can be both an advantage and a disadvantage, depending on your specific needs and preferences.
Standardized Systems
Commercial solar providers typically offer standardized system designs that have been tested and proven effective. While this limits your ability to create a highly personalized setup, it also ensures that you’re getting a reliable and efficient system.
- Pre-designed packages simplify the decision-making process
- Proven configurations reduce the risk of system inefficiencies
- Standardization often leads to faster installation times
Aesthetics and Roof Compatibility
One area where limited customization can be particularly noticeable is in the aesthetics of your solar installation. Commercial systems may not always blend seamlessly with your home’s architecture or your personal style preferences.
- Panel colors and styles may be restricted to what the company offers
- Mounting options might be limited, potentially affecting the visual impact on your roof
- Roof compatibility issues may arise if your home has an unusual roof shape or material
System Size Constraints
Commercial solar providers often work with specific system sizes, which may not perfectly match your energy needs. This can result in either slightly oversized or undersized systems.
| System Size | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Oversized | Future-proof, potential for energy credits | Higher initial cost, possible regulatory issues |
| Undersized | Lower upfront cost, easier approval | May not meet all energy needs, limited expansion options |
Technology Options
While commercial solar companies stay up-to-date with the latest solar technologies, your choices may be limited to what they currently offer.
- You may not have access to cutting-edge or experimental solar technologies
- Battery storage options might be restricted to specific brands or capacities
- Inverter choices could be limited to the company’s preferred suppliers
B. Higher upfront costs
One of the most significant considerations when opting for commercial solar power is the higher upfront cost compared to DIY solutions. This initial investment can be a hurdle for some homeowners, but it’s essential to consider the long-term benefits and potential savings.
Initial Investment Breakdown
Understanding where your money goes can help you appreciate the value of a commercial solar installation:
- Solar panels (typically 25-30% of total cost)
- Inverter (10-20% of total cost)
- Balance of system components (racking, wiring, etc.)
- Labor and installation costs
- Permits and inspections
- Design and engineering fees
Financing Options
To help manage the higher upfront costs, many commercial solar providers offer financing options:
- Solar loans: Allow you to spread the cost over time, often with competitive interest rates
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): You pay for the electricity produced, not the system itself
- Solar leases: Rent the system for a fixed monthly fee
Return on Investment (ROI)
While the initial cost may be higher, commercial solar power often provides a better ROI in the long run:
- Professional installations typically have higher efficiency rates
- Reduced risk of system failures or underperformance
- Potential for increased home value
Tax Incentives and Rebates
Commercial solar installations usually qualify for various financial incentives:
- Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC): Currently allows you to deduct 30% of the cost of installing a solar energy system from your federal taxes
- State and local rebates: Many areas offer additional incentives to encourage solar adoption
- Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs): In some states, you can earn and sell these certificates for additional income
C. Warranty and maintenance support
One of the most significant advantages of choosing commercial solar power is the comprehensive warranty and maintenance support that typically comes with your installation. This peace of mind can be invaluable, especially if you’re not confident in your ability to troubleshoot and maintain a solar system on your own.
Types of Warranties
Commercial solar installations often come with multiple types of warranties:
- Equipment Warranty: Covers defects in the solar panels, inverters, and other hardware
- Performance Warranty: Guarantees a certain level of energy production over time
- Workmanship Warranty: Covers issues related to the installation process
Here’s a comparison of typical warranty lengths for different components:
| Component | Typical Warranty Length |
| Solar Panels | 25-30 years |
| Inverters | 10-25 years |
| Racking System | 10-20 years |
| Workmanship | 5-10 years |
Maintenance Support
Commercial solar providers often offer ongoing maintenance support, which can include:
- Regular system check-ups and performance monitoring
- Cleaning services to ensure optimal panel efficiency
- Rapid response to any system issues or failures
- Software updates for inverters and monitoring systems
Benefits of Professional Support
Having professional warranty and maintenance support offers several advantages:
- Reduced stress: You don’t have to worry about diagnosing or fixing issues yourself
- Time-saving: Professionals can quickly identify and resolve problems
- Improved system longevity: Regular maintenance can extend the life of your solar installation
- Optimized performance: Professionals can fine-tune your system for maximum efficiency
Potential Drawbacks
While warranty and maintenance support is generally a positive aspect, there are a few potential drawbacks to consider:
- Some warranties may have specific conditions that could limit coverage
- You may be locked into using the same company for repairs and maintenance
- Extended warranties or premium service plans might come at an additional cost
D. Professional installation and expertise
One of the most compelling reasons to choose commercial solar power is the access to professional installation and expertise. This aspect can significantly impact the performance, safety, and longevity of your solar power system.
Benefits of Professional Installation
When you opt for commercial solar power, you’re tapping into a wealth of knowledge and experience. Here are some key benefits:
- Proper system design: Professionals can optimize your system based on your roof orientation, shading, and local climate conditions
- Code compliance: Installers ensure your system meets all local building codes and electrical standards
- Safety: Professional installations minimize the risk of roof damage, electrical fires, and other potential hazards
- Efficiency: Experienced installers can complete the job more quickly and with fewer errors than a DIY approach
- Equipment handling: Professionals have the tools and knowledge to safely transport and install delicate solar equipment
Expertise Throughout the Process
Commercial solar providers offer expertise at every stage of your solar journey:
- Initial assessment: Professionals can accurately evaluate your energy needs and site suitability
- System design: Expert designers create a custom solution tailored to your specific situation
- Permitting: Installers handle all necessary paperwork and inspections
- Installation: Skilled technicians ensure proper mounting, wiring, and connection to the grid
- Post-installation support: Ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal performance
Quality Assurance
Professional installations often come with quality assurance measures:
- Rigorous testing of the system before and after installation
- Adherence to industry best practices and manufacturer guidelines
- Use of specialized tools and equipment for precise installation
- Quality control checks throughout the installation process
Potential Drawbacks of Professional Installation
While the benefits are numerous, there are a few potential drawbacks to consider:
- Higher cost: Professional labor and expertise come at a premium
- Less hands-on involvement: If you enjoy DIY projects, you may feel less connected to the process
- Scheduling dependencies: You’ll need to work around the installer’s schedule
- Potential for overselling: Some companies may try to upsell you on unnecessary features or larger systems
Choosing the Right Installer
If you decide to go with commercial solar power, selecting the right installer is crucial. Here are some factors to consider:
- Experience and track record in the industry
- Certifications and licenses (e.g., NABCEP certification)
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Warranty and after-installation support offerings
- Transparency in pricing and system design
The Installation Process
Understanding the professional installation process can help you appreciate the value of commercial solar power:
- Site assessment: A thorough evaluation of your property and energy needs
- System design: Creation of a custom solar solution based on the assessment
- Permitting: Handling all necessary paperwork and approvals
- Equipment procurement: Sourcing high-quality components for your system
- Installation: Typically completed in 1-3 days for residential systems
- Inspection: Final checks by both the installer and local authorities
- Grid connection: Coordinating with your utility company for proper integration
- System activation: Turning on your solar power system and monitoring initial performance
By choosing commercial solar power, you’re investing in a turn-key solution that leverages professional expertise to ensure a high-quality, efficient, and safe solar installation. While it may come at a higher upfront cost, the peace of mind and potential for optimized performance can make it a worthwhile investment for many homeowners.
Now that you understand the advantages and disadvantages of commercial solar power, it’s time to consider the various factors that will influence your decision between DIY and commercial options. In the next section, we’ll explore these crucial factors to help you make an informed choice for your solar energy journey.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
Now that we’ve explored the pros and cons of both DIY and commercial solar power options, it’s time to dive into the crucial factors you need to consider when making your decision. Your choice between DIY and commercial solar power will significantly impact your energy future, so it’s essential to weigh these factors carefully.
A. Long-term goals and energy needs
When deciding between DIY and commercial solar power, you must first consider your long-term goals and energy needs. This consideration is crucial as it will shape the scale and scope of your solar project.
Assessing your current energy consumption
To begin, you should analyze your current energy consumption. Here’s how you can do this:
- Review your past 12 months of electricity bills
- Calculate your average monthly energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh)
- Identify any seasonal variations in your energy consumption
- Note any planned changes that might affect your future energy needs (e.g., purchasing an electric vehicle, adding a home office)
Projecting future energy needs
Once you have a clear picture of your current energy consumption, it’s time to project your future needs. Consider the following:
- Are you planning any home additions or renovations?
- Do you expect your family size to change?
- Are you considering the purchase of energy-intensive appliances or electric vehicles?
- Do you anticipate any lifestyle changes that could impact your energy consumption?
Setting your energy independence goals
Next, you need to determine your energy independence goals. Ask yourself:
- Do you want to completely eliminate your reliance on the grid?
- Are you aiming to reduce your energy bills by a certain percentage?
- Is your goal to have a backup power source during outages?
Your answers to these questions will help you decide whether a DIY or commercial solar solution is more appropriate. For instance, if you’re aiming for complete energy independence, a commercial system might be more suitable due to its higher capacity and efficiency.
Considering scalability
Another crucial aspect to consider is the scalability of your solar system. Your energy needs may change over time, so you should think about whether you want a system that can be easily expanded.
| Aspect | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Initial Size | Generally smaller | Can be customized to any size |
| Expandability | May be limited by initial design | Often designed with future expansion in mind |
| Compatibility | Expansion may require matching components | Professional design ensures compatibility |
| Cost of Expansion | Can be cost-effective for small additions | May offer economies of scale for larger expansions |
B. Local regulations and permits
Before you embark on your solar journey, it’s crucial to understand and navigate the local regulations and permit requirements. These can significantly impact your choice between DIY and commercial solar installations.
Understanding local zoning laws
Zoning laws can affect where and how you can install solar panels on your property. Some key points to consider include:
- Roof vs. ground-mounted systems: Some areas may have restrictions on ground-mounted systems.
- Setback requirements: There may be rules about how close to property lines you can install panels.
- Height restrictions: Some localities limit how high solar panels can extend above your roof.
- Historic district regulations: If you live in a historic district, there may be additional rules about solar panel visibility.
Navigating permit requirements
Permit requirements can vary widely depending on your location. Here’s what you need to know:
- Building permits: Most localities require a building permit for solar installations.
- Electrical permits: You’ll likely need a separate electrical permit for the wiring work.
- Fire safety requirements: Some areas have specific fire safety regulations for solar installations.
- Utility interconnection approval: If you’re connecting to the grid, you’ll need approval from your local utility company.
DIY vs. Commercial: Handling regulations and permits
When it comes to dealing with regulations and permits, there are significant differences between DIY and commercial installations:
| Aspect | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Knowledge of local laws | You must research and understand all applicable laws | Installers are usually well-versed in local regulations |
| Permit application | You’re responsible for all paperwork | Company handles permit applications |
| Liability | You bear all liability for compliance | Company assumes liability for compliance |
| Inspection process | You must coordinate and be present for inspections | Company manages the inspection process |
| Time investment | Can be significant | Minimal time required from you |
Incentives and rebates
Local and state incentives can significantly impact the cost-effectiveness of your solar installation. These may include:
- Tax credits
- Rebates
- Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs)
- Performance-based incentives
It’s important to note that some incentives may only be available for professionally installed systems, which could influence your decision between DIY and commercial options.
C. Time availability
The time you have available to dedicate to your solar project is a crucial factor in deciding between DIY and commercial installations. Let’s break down the time commitments for each option.
DIY solar time commitment
If you choose the DIY route, be prepared to invest a significant amount of time in your project. Here’s a breakdown of the time you might need to allocate:
- Research and planning: 40-80 hours
- Understanding solar technology
- Designing your system
- Selecting components
- Learning about safety procedures
- Permitting and paperwork: 10-20 hours
- Researching local regulations
- Preparing and submitting permit applications
- Coordinating with local authorities
- Procurement: 5-10 hours
- Sourcing components
- Comparing prices
- Ordering materials
- Installation: 40-100 hours (depending on system size and complexity)
- Mounting racking system
- Installing solar panels
- Wiring the system
- Setting up inverters and other components
- Inspection and grid connection: 5-10 hours
- Coordinating with inspectors
- Arranging utility company connection
- Ongoing maintenance: 2-4 hours per month
- Regular cleaning
- System checks
- Troubleshooting
Commercial solar time commitment
Opting for a commercial installation significantly reduces your time investment. Here’s what you can expect:
- Initial consultation: 1-2 hours
- Meeting with solar companies
- Discussing your needs and goals
- System design approval: 1-2 hours
- Reviewing proposed designs
- Providing feedback
- Site assessment: 1-2 hours
- Being present for the professional site evaluation
- Installation: Minimal time required from you
- The installation team handles everything
- Final inspection and activation: 1-2 hours
- Being present for final inspection
- Learning about system operation
- Ongoing maintenance: Minimal to none
- Most commercial installations include maintenance services
Comparing time commitments
| Aspect | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Total time investment | 100-220+ hours | 4-8 hours |
| Flexibility | Work at your own pace | Scheduled by the installation company |
| Learning curve | Steep – requires significant study | Minimal – experts handle the details |
| Ongoing time commitment | Regular maintenance required | Little to no ongoing time investment |
D. Technical skills and knowledge
Your level of technical expertise plays a crucial role in determining whether a DIY or commercial solar installation is right for you. Let’s explore the skills and knowledge required for each option.
DIY solar: Required technical skills
If you’re considering a DIY solar installation, you’ll need a diverse set of technical skills:
- Electrical knowledge
- Understanding of DC and AC electrical systems
- Ability to read and create electrical diagrams
- Familiarity with National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements
- Roofing and construction skills
- Experience with roof structures and materials
- Ability to safely work at heights
- Knowledge of weatherproofing techniques
- Solar technology expertise
- Understanding of photovoltaic systems
- Knowledge of solar panel types and efficiencies
- Familiarity with inverters, charge controllers, and batteries
- Project management abilities
- Skill in coordinating various aspects of the installation
- Ability to manage timelines and budgets
- Problem-solving skills
- Capacity to troubleshoot issues during installation and operation
- Adaptability to unexpected challenges
Commercial solar: Required technical knowledge
While you don’t need to be a solar expert for a commercial installation, some basic knowledge is beneficial:
- Solar basics
- Understanding of how solar energy works
- Familiarity with key components of a solar system
- Energy consumption awareness
- Ability to analyze your energy usage patterns
- Understanding of how solar production aligns with your consumption
- Financial literacy
- Comprehension of solar financing options
- Ability to understand and compare quotes
- Basic electrical knowledge
- Understanding of your home’s electrical system
- Awareness of energy efficiency principles
Skill level comparison
| Skill Area | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Electrical | Advanced knowledge required | Basic understanding helpful |
| Construction | Hands-on experience needed | No skills required |
| Solar technology | In-depth expertise necessary | General awareness beneficial |
| Project management | Strong skills required | Minimal involvement needed |
| Problem-solving | Must be highly proficient | Not essential |
Learning resources for DIY solar
If you’re leaning towards DIY but need to build your skills, consider these learning resources:
- Online courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer solar energy courses.
- Local workshops: Check community colleges or solar organizations for hands-on training.
- Books and manuals: There are numerous comprehensive guides on DIY solar installation.
- Online forums and communities: Websites like SolarPanelTalk.com offer valuable peer support.
- YouTube tutorials: Many experienced DIYers share detailed installation videos.
Remember, while these resources can provide valuable information, they’re not a substitute for professional training and experience. Always prioritize safety and consult professionals when in doubt.
E. Budget constraints
Your budget is often the deciding factor between DIY and commercial solar installations. Let’s break down the financial aspects of both options to help you make an informed decision.
Initial costs: DIY vs. Commercial
The upfront costs for solar installations can vary significantly between DIY and commercial options:
| Cost Component | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Equipment | $1.00 – $1.50 per watt | $2.00 – $3.00 per watt |
| Labor | $0 (your time) | $0.50 – $1.00 per watt |
| Permits and inspections | $200 – $500 (your time for paperwork) | Included in total cost |
| Design and engineering | Your time | Included in total cost |
| Total cost per watt | $1.00 – $1.50 | $2.50 – $4.00 |
For a typical 5kW system:
- DIY cost: $5,000 – $7,500
- Commercial cost: $12,500 – $20,000
Hidden costs to consider
When budgeting for your solar project, be aware of these potential hidden costs:
- Tools and equipment: DIY installations may require specialized tools.
- Shipping costs: Large solar components can have significant shipping fees.
- Structural reinforcements: Your roof may need upgrades to support the solar panels.
- Electrical system upgrades: You might need to update your home’s electrical panel.
- Mistakes and rework: DIY errors can lead to additional expenses.
- Extended warranties: Commercial installations often include comprehensive warranties.
Financing options
The availability and terms of financing can impact your choice:
- Cash purchase
- DIY: Requires full upfront payment
- Commercial: May offer a cash discount
- Solar loans
- DIY: Limited options, may require personal loans
- Commercial: Often offered through the installation company
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and leases
- DIY: Not applicable
- Commercial: Can eliminate upfront costs
- Home equity loans or lines of credit
- Applicable to both DIY and commercial installations
- May offer tax-deductible interest
Long-term financial considerations
When evaluating your budget, consider these long-term factors:
- Energy savings
- Both DIY and commercial systems will reduce your electricity bills
- Commercial systems may be more efficient, leading to greater savings
- Maintenance costs
- DIY: You’re responsible for all maintenance and repairs
- Commercial: Often includes maintenance plans and warranties
- System lifespan and degradation
- DIY: May have shorter lifespan due to potential installation issues
- Commercial: Professional installation can ensure optimal performance and longevity
- Home value increase
- Both can increase home value, but professional installations may be more attractive to buyers
- Insurance costs
- DIY: May increase home insurance premiums
- Commercial: Often covered under existing home insurance policies
Return on Investment (ROI) comparison
To help you understand the long-term financial impact, let’s compare the ROI for DIY and commercial installations:
| Factor | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Initial cost (5kW system) | $7,500 | $17,500 |
| Annual energy production | 6,500 kWh | 7,000 kWh |
| Annual savings (at $0.13/kWh) | $845 | $910 |
| System lifespan | 20-25 years | 25-30 years |
| Maintenance costs (annual) | $100 | Included in warranty |
| Warranty | Variable (component-specific) | 25 years (typically) |
| Estimated payback period | 8-10 years | 12-15 years |
| 25-year savings | $13,625 – $18,625 | $20,250 – $25,250 |
While DIY systems have a lower initial cost and faster payback period, commercial systems often provide greater long-term savings due to higher efficiency and longer lifespans.
When considering your budget constraints, remember to factor in both the short-term costs and long-term financial implications. While a DIY system may seem more budget-friendly initially, a commercial system could provide better value over time, especially when you consider the expertise, warranties, and peace of mind that come with professional installation.
As we move forward, it’s important to carefully weigh these factors against your personal circumstances, skills, and goals. In the next section, we’ll delve into the assessment of your specific energy needs, which will further guide your decision between DIY and commercial solar power options.
Assessing Your Energy Needs
Now that you’ve explored the pros and cons of DIY and commercial solar power options, it’s time to dive into a crucial step in your solar journey: assessing your energy needs. Understanding your energy consumption is fundamental to making an informed decision about which solar power solution is right for you. Let’s break down this process into manageable steps that will help you determine the optimal solar system size for your home or business.
Calculating current energy consumption
To accurately assess your energy needs, you’ll need to start by calculating your current energy consumption. This step is crucial because it forms the foundation for determining the size and capacity of the solar system you’ll require. Here’s how you can go about it:
- Review your electricity bills: Gather your electricity bills from the past 12 months. This will give you a comprehensive view of your energy usage throughout the year, accounting for seasonal variations.
- Find your average monthly consumption: Add up the kilowatt-hours (kWh) used for each month and divide by 12 to get your average monthly consumption.
- Calculate your daily usage: Divide your average monthly consumption by 30 to get your average daily usage in kWh.
- Consider peak usage periods: Identify months with higher energy consumption. This could be due to increased air conditioning use in summer or heating in winter.
- Use online energy calculators: Many utility companies and solar providers offer online tools to help you estimate your energy consumption based on your appliances and usage patterns.
- Install an energy monitor: For a more accurate assessment, consider installing an energy monitor. These devices provide real-time data on your energy consumption, helping you identify energy-hungry appliances and usage patterns.
Here’s a simple table to help you organize your energy consumption data:
| Month | Energy Consumption (kWh) |
| January | X |
| February | X |
| March | X |
| April | X |
| May | X |
| June | X |
| July | X |
| August | X |
| September | X |
| October | X |
| November | X |
| December | X |
| Total | Sum of all months |
| Monthly Average | Total ÷ 12 |
| Daily Average | Monthly Average ÷ 30 |
By following these steps, you’ll gain a clear picture of your current energy consumption. This information is invaluable as you move forward in your solar power journey.
Determining optimal system size
Once you have a solid understanding of your energy consumption, the next step is to determine the optimal size for your solar power system. This is where things get a bit more technical, but don’t worry – we’ll break it down for you.
- Consider your available roof space: The amount of roof space you have will play a significant role in determining the size of your solar system. Measure the area of your roof that receives direct sunlight for most of the day. Remember, solar panels are typically about 65 inches by 39 inches, so you’ll need to calculate how many can fit in your available space.
- Assess your roof’s orientation and tilt: The direction your roof faces and its angle can affect the efficiency of your solar panels. South-facing roofs in the Northern Hemisphere are ideal, but east and west-facing roofs can also work well. The optimal tilt angle is usually equal to your latitude, but this can vary based on local conditions.
- Factor in local weather patterns: Your location’s average sunlight hours and weather patterns will impact your system’s efficiency. Areas with more cloudy days might require larger systems to generate the same amount of power as sunnier regions.
- Calculate your energy production needs: Based on your daily energy consumption, you’ll need to determine how much energy your solar system should produce. As a general rule, you’ll want your system to generate slightly more than your average daily consumption to account for inefficiencies and potential future increases in energy use.
- Use the PVWatts Calculator: The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) offers a free online tool called PVWatts that can help you estimate the energy production and cost of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) energy systems throughout the world. This tool takes into account your location, system size, and other factors to give you a more accurate estimate.
- Consider battery storage: If you’re planning to go off-grid or want to have backup power during outages, you’ll need to factor in battery storage. This will increase the size and cost of your system but provide greater energy independence.
Here’s a simple formula to help you estimate your system size:
System size (in kW) = (Daily energy use in kWh × 1.15) ÷ (Peak sun hours × 0.75)
The 1.15 factor accounts for system losses, while the 0.75 factor represents the average efficiency of solar panels. Peak sun hours vary by location but typically range from 3 to 6 hours per day.
Let’s look at an example:
| Factor | Value |
| Daily energy use | 30 kWh |
| Peak sun hours | 5 |
| Calculation | (30 × 1.15) ÷ (5 × 0.75) |
| Result | 9.2 kW system |
In this example, a home using 30 kWh per day in an area with 5 peak sun hours would need approximately a 9.2 kW solar system.
Remember, this is a rough estimate. Factors like panel efficiency, inverter choice, and local regulations can all impact the final system size. It’s always best to consult with a solar professional for a more accurate assessment.
Estimating future energy requirements
While understanding your current energy needs is crucial, it’s equally important to consider your future energy requirements. Your solar power system is a long-term investment, typically lasting 25-30 years, so you’ll want to ensure it can meet your energy needs not just now, but in the years to come.
Here are some factors to consider when estimating your future energy requirements:
- Family growth: If you’re planning to expand your family, your energy consumption is likely to increase. More people in the house typically means more appliances running, more hot water usage, and generally higher energy consumption.
- Home additions or renovations: Are you planning to add a room, build a home office, or finish your basement? These changes can significantly impact your energy needs.
- New appliances or technologies: As technology advances, you might be considering adding new appliances or smart home devices. While many new appliances are more energy-efficient, adding more devices can increase your overall energy consumption.
- Electric vehicle adoption: If you’re thinking about purchasing an electric vehicle in the future, this will substantially increase your electricity usage. A typical EV can add 2,000-5,000 kWh to your annual electricity consumption.
- Lifestyle changes: Major life changes like retirement or working from home can alter your energy consumption patterns.
- Energy efficiency improvements: On the flip side, you might be planning to improve your home’s energy efficiency through better insulation, LED lighting, or more efficient appliances. These changes could reduce your future energy needs.
To estimate your future energy requirements, consider creating a table like this:
| Factor | Estimated Annual Impact (kWh) |
| Family growth | +500 |
| Home office addition | +1,000 |
| New appliances | +800 |
| Electric vehicle | +3,000 |
| Energy efficiency improvements | -1,000 |
| Total Estimated Increase | 4,300 |
In this example, the homeowner estimates their annual energy consumption could increase by 4,300 kWh in the coming years. This would translate to an additional 11.8 kWh per day (4,300 ÷ 365), which should be factored into the solar system size calculation.
It’s generally recommended to add about 20-25% to your current energy needs to account for future increases. However, if you have specific plans that will significantly impact your energy consumption, you might want to adjust this percentage accordingly.
When estimating future energy requirements, keep these tips in mind:
- Be realistic: While it’s good to plan for the future, avoid overestimating your needs too drastically. An oversized system can be less efficient and more expensive than necessary.
- Consider energy efficiency first: Before increasing your system size, look for ways to reduce your energy consumption. Improving your home’s energy efficiency can be a cost-effective way to manage your energy needs.
- Plan for scalability: If you’re unsure about future needs, consider a system that allows for easy expansion. Some inverters can accommodate additional panels, allowing you to increase your system’s capacity later if needed.
- Consult with professionals: Solar installers and energy auditors can provide valuable insights into future energy trends and help you make more accurate predictions.
- Review utility policies: Check if your utility company allows net metering or has caps on system sizes. These factors can influence how you plan for future energy needs.
By carefully assessing your current energy consumption, determining the optimal system size, and estimating your future energy requirements, you’ll be well-equipped to choose the right solar power solution for your needs. Whether you decide to go the DIY route or opt for a commercial installation, this thorough assessment will ensure your solar power system is tailored to your specific situation, maximizing your energy independence and return on investment.
As you move forward in your solar power journey, keep in mind that this assessment is just one piece of the puzzle. In the next section, we’ll delve into the financial considerations of solar power, helping you understand the costs, savings, and potential return on investment for both DIY and commercial solar installations.
Financial Considerations
As you weigh your options between DIY and commercial solar power, it’s crucial to dive deep into the financial aspects of each choice. Understanding the economic implications will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and long-term financial goals. Let’s explore the key financial considerations that will shape your solar power journey.
A. Return on Investment Analysis
When it comes to solar power, return on investment (ROI) is a critical factor in your decision-making process. Both DIY and commercial solar installations offer potential returns, but the tim
Installation Process Comparison
Now that we’ve examined the various factors to consider when choosing between DIY and commercial solar power, let’s dive into the installation process for each option. Understanding the installation process is crucial in making an informed decision about which route to take for your solar power needs.
A. Required tools and equipment
When it comes to installing solar panels, the tools and equipment needed can vary significantly between DIY and commercial installations. Let’s break down what you’ll need for each approach:
DIY Solar Installation Tools and Equipment
If you’re considering a DIY solar installation, you’ll need to gather a variety of tools and equipment. Here’s a comprehensive list of what you might need:
- Solar panels
- Inverter (string inverter or microinverters)
- Mounting system (roof mounts or ground mounts)
- Electrical wiring and connectors
- Charge controller (for off-grid systems)
- Batteries (for off-grid or hybrid systems)
- Ladder or scaffolding
- Drill and drill bits
- Screwdriver set
- Wire strippers and crimpers
- Multimeter
- Angle grinder (for cutting mounting rails)
- Hammer and nails
- Level
- Tape measure
- Safety equipment (gloves, safety glasses, hard hat)
- Sealant for roof penetrations
Keep in mind that this list may vary depending on your specific installation requirements and the type of system you’re installing.
Commercial Solar Installation Tools and Equipment
Commercial solar installations typically involve more specialized and heavy-duty equipment. While you won’t need to worry about acquiring these tools yourself, it’s helpful to understand what goes into a professional installation:
- Solar panels (often higher capacity than residential panels)
- Commercial-grade inverters
- Heavy-duty mounting systems
- Industrial-grade electrical components
- Specialized lifts or cranes for panel placement
- Professional-grade testing equipment
- Advanced monitoring systems
- Large-scale battery storage systems (if applicable)
- Custom racking systems for optimal panel placement
- Specialized tools for working with high-voltage systems
Commercial installers have access to professional-grade equipment that ensures efficient and safe installation of large-scale solar systems.
| Aspect | DIY Installation | Commercial Installation |
| Tools Required | Basic hand tools, power tools, and safety equipment | Specialized industrial equipment and professional-grade tools |
| Equipment Complexity | Generally simpler, residential-grade components | More complex, commercial-grade components |
| Scale of Equipment | Suitable for small to medium residential installations | Designed for large-scale commercial or industrial installations |
| Accessibility | Readily available at hardware stores or online retailers | Often proprietary or only available to licensed professionals |
| Cost of Tools/Equipment | Lower initial investment, but you’re responsible for purchases | Higher cost, but included in the installation service |
B. Commercial installation timeline
The timeline for a commercial solar installation can vary depending on the size and complexity of the project. However, here’s a general overview of what you can expect:
- Initial Consultation and Site Assessment (1-2 weeks)
- Meeting with solar providers
- Site evaluation and energy needs assessment
- System Design and Proposal (2-4 weeks)
- Custom system design based on your energy needs and site conditions
- Proposal preparation and presentation
- Contract Signing and Permitting (4-8 weeks)
- Review and signing of the contract
- Submission of permit applications to local authorities
- Approval process (timeline can vary significantly based on location)
- Equipment Procurement (2-6 weeks)
- Ordering of solar panels, inverters, and other necessary components
- Delivery of equipment to the installation site
- Installation (1-2 weeks for residential, 4-8 weeks for larger commercial projects)
- Site preparation
- Mounting system installation
- Solar panel placement
- Electrical wiring and inverter installation
- Inspection and Utility Connection (2-4 weeks)
- Local building department inspection
- Utility company inspection and meter installation
- System Activation and Monitoring Setup (1-2 days)
- Final testing of the system
- Activation and connection to the grid
- Setting up monitoring systems
Total timeline: Typically 3-6 months for residential installations, 6-12 months for larger commercial projects
It’s important to note that these timelines can vary significantly based on factors such as:
- Project size and complexity
- Local permitting processes
- Equipment availability
- Weather conditions during installation
- Utility company responsiveness
Commercial solar installers are experienced in managing these timelines and can often work efficiently to complete projects within the expected timeframe. They handle all aspects of the installation process, from initial design to final activation, ensuring a smooth and professional experience.
C. DIY step-by-step overview
If you’re considering a DIY solar installation, it’s crucial to understand the steps involved. While the process can be rewarding, it’s also complex and requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a detailed step-by-step overview of a typical DIY solar installation:
- Research and Planning (4-8 weeks)
- Learn about solar technology and local regulations
- Assess your energy needs and roof suitability
- Design your solar system (panel layout, wiring diagrams)
- Research and select components (panels, inverters, mounting systems)
- Obtain Permits and Approvals (2-6 weeks)
- Contact your local building department
- Submit system plans and apply for necessary permits
- Schedule inspections as required
- Purchase Equipment (2-4 weeks)
- Order solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and other components
- Ensure all necessary tools are available
- Prepare for Installation (1-2 days)
- Clear the work area
- Ensure safety equipment is ready
- Review installation plans and instructions
- Install Mounting System (1-3 days)
- Locate roof rafters and mark mounting points
- Install flashing and mounting brackets
- Secure rails to mounting brackets
- Install Solar Panels (1-2 days)
- Carefully lift panels onto the roof
- Attach panels to mounting rails
- Connect panel wiring (in series or parallel as per your design)
- Install Inverter and Electrical Components (1-2 days)
- Mount the inverter in a suitable location (often near the main electrical panel)
- Install DC disconnect switch between panels and inverter
- Install AC disconnect switch between inverter and main panel
- Complete Electrical Wiring (1-2 days)
- Run conduit from panels to inverter and from inverter to main panel
- Pull wires through conduit
- Make all necessary electrical connections
- Ground the system according to local codes
- Install Monitoring System (if applicable) (1 day)
- Set up the monitoring hardware
- Configure software and connect to your home network
- Final Checks and Testing (1 day)
- Double-check all connections and mounting hardware
- Test system voltage and performance
- Ensure proper system grounding
- Inspections and Utility Connection (2-4 weeks)
- Schedule and pass local building department inspection
- Arrange for utility company inspection and meter installation
- System Activation (1 day)
- Turn on the system and monitor initial performance
- Configure any monitoring apps or software
Total DIY timeline: Typically 3-6 months, depending on your experience level and time commitment
It’s important to note that this timeline can vary significantly based on your experience, the complexity of your installation, and how much time you can dedicate to the project. Many DIY installers find that the process takes longer than initially anticipated, especially if they encounter unexpected challenges or need to learn new skills along the way.
Here’s a comparison of key aspects between DIY and commercial solar installations:
| Aspect | DIY Installation | Commercial Installation |
| Timeline | 3-6 months (can be longer) | 3-6 months (residential), 6-12 months (larger commercial) |
| Labor | Self-performed, potentially with help from friends or family | Professional team with specialized skills |
| Skill Level Required | High – requires electrical, construction, and solar knowledge | Minimal for you – experts handle everything |
| Project Management | You manage all aspects of the project | Handled by the solar company |
| Customization | High – you have complete control over system design | Moderate – designed by professionals with your input |
| Risk | Higher risk of errors or safety issues | Lower risk due to professional expertise |
| Warranty | Individual component warranties only | Often includes comprehensive system warranty |
| Permitting & Paperwork | You handle all permitting and utility paperwork | Typically handled by the installation company |
When deciding between DIY and commercial solar installation, consider your skills, available time, and comfort level with taking on a complex project. While DIY can be more cost-effective, it requires a significant investment of time and effort. Commercial installations, on the other hand, offer the convenience of professional expertise and typically faster completion times.
As you weigh your options, remember that the installation process is just one part of your solar journey. The next crucial aspect to consider is the ongoing maintenance and upkeep of your solar power system. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of your investment, whether you choose the DIY or commercial route.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Now that we’ve explored the installation process for both DIY and commercial solar power systems, it’s crucial to understand the ongoing maintenance and upkeep required to keep your solar panels operating at peak efficiency. Whether you’ve chosen the DIY route or opted for a commercial installation, proper maintenance is key to maximizing your solar power investment and ensuring long-term performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the most well-designed solar power systems can encounter problems from time to time. Being able to identify and address these issues quickly can save you time, money, and frustration. Here are some common problems you might face with your solar panels and how to troubleshoot them:
1. Reduced Energy Output
If you notice a significant drop in your system’s energy production, several factors could be at play:
- Dirty panels: Dust, pollen, and debris can accumulate on your panels, reducing their efficiency. Regular cleaning can often resolve this issue.
- Shading: New obstructions like tree growth or nearby construction can cast shadows on your panels. Assess your panels’ surroundings and consider trimming trees or adjusting panel placement if necessary.
- Inverter problems: The inverter is crucial for converting DC power to AC power. Check if the inverter’s lights indicate normal operation or if there are any error codes displayed.
- Loose connections: Wiring issues can lead to power loss. Inspect visible connections for any signs of damage or looseness.
2. Inverter Shutdown
If your inverter frequently shuts down or displays error messages, try these steps:
- Reset the inverter by turning it off and on again.
- Check for any visible damage to the inverter or surrounding wiring.
- Ensure proper ventilation around the inverter to prevent overheating.
- Consult your inverter’s manual for specific error code meanings and recommended actions.
3. Faulty Monitoring System
Your monitoring system helps you track your solar panel performance. If it’s not working correctly:
- Check your internet connection to ensure the system can transmit data.
- Verify that all monitoring equipment is powered on and properly connected.
- Update the monitoring software or app to the latest version.
- Contact your monitoring system provider for technical support if issues persist.
4. Physical Damage
Severe weather, falling debris, or animal activity can potentially damage your solar panels. Regularly inspect your panels for:
- Cracks or chips in the glass
- Loose or damaged mounting hardware
- Signs of water infiltration
- Chewed wiring (often caused by rodents)
If you notice any physical damage, it’s best to consult a professional for repair or replacement to avoid safety hazards and maintain your warranty.
5. Hot Spots
Hot spots occur when a portion of a solar panel overheats, potentially causing damage and reducing efficiency. Signs of hot spots include:
- Discoloration on the panel surface
- Burn marks
- Melted areas
If you suspect hot spots, have your system inspected by a professional immediately to prevent further damage.
Commercial Service Agreements
For those who’ve opted for a commercial solar installation, service agreements play a crucial role in maintaining your system’s performance and longevity. These agreements typically offer several benefits:
- Regular Inspections: Most commercial service agreements include scheduled inspections to catch potential issues before they become major problems.
- Performance Monitoring: Advanced monitoring systems track your solar panel output, alerting technicians to any unexpected drops in efficiency.
- Cleaning Services: Many agreements include periodic panel cleaning to maintain optimal energy production.
- Prompt Repairs: When issues arise, commercial providers often guarantee quick response times for repairs, minimizing downtime.
- Warranty Management: Service providers handle warranty claims on your behalf, simplifying the process if components need replacement.
- Software Updates: As inverter and monitoring technology evolves, service agreements often include software updates to keep your system current.
- Annual Performance Reports: Detailed reports help you understand your system’s performance and identify any long-term trends or issues.
When evaluating commercial service agreements, consider the following factors:
| Factor | Description | Importance |
| Coverage Scope | What specific services are included? | High |
| Response Time | How quickly will technicians address issues? | High |
| Cost | Is the fee structure fixed or variable? | Medium |
| Contract Length | How long are you committed to the agreement? | Medium |
| Scalability | Can the agreement adapt if you expand your system? | Low to Medium |
| Cancellation Terms | What are the conditions for ending the agreement? | Low |
It’s essential to carefully review and compare service agreements from different providers. While they may seem like an additional expense, a well-structured agreement can save you money in the long run by maintaining your system’s efficiency and preventing costly repairs.
DIY Maintenance Responsibilities
If you’ve chosen the DIY route for your solar power system, you’ll need to take a more hands-on approach to maintenance. Here’s a comprehensive guide to keeping your DIY solar system in top shape:
1. Regular Cleaning
Keeping your solar panels clean is one of the most important maintenance tasks you can perform:
- Frequency: Clean your panels at least twice a year, or more frequently if you live in a dusty area or near trees.
- Timing: Clean early in the morning or on an overcast day to avoid working with hot panels.
- Method: Use a soft brush or sponge with mild soap and water. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
- Safety: If your panels are on the roof, consider hiring a professional cleaner to avoid accidents.
2. Visual Inspections
Conduct monthly visual inspections of your system:
- Check for any physical damage to panels, wiring, or mounting hardware.
- Look for signs of animal activity, such as nesting or chewed wiring.
- Ensure that no new shade sources have appeared (e.g., tree growth).
- Verify that all indicator lights on your inverter and monitoring system are functioning normally.
3. Performance Monitoring
Regularly review your system’s performance data:
- Set up alerts in your monitoring system for significant drops in production.
- Compare your monthly energy production to previous years, accounting for seasonal variations.
- Keep a log of your system’s performance to identify long-term trends.
4. Inverter Maintenance
Your inverter requires specific attention:
- Keep the area around the inverter clean and well-ventilated.
- Check for and clear any debris from cooling fins or vents.
- Listen for unusual noises that might indicate fan problems.
- Note any error codes and consult your manual or online resources for troubleshooting.
5. Wiring and Connection Checks
Periodically inspect all visible wiring and connections:
- Look for signs of corrosion, particularly on outdoor connections.
- Ensure all cable ties and conduits are intact and properly securing wires.
- Check that junction boxes are sealed and watertight.
- If you notice any issues with wiring, consult a licensed electrician for safety.
6. Battery Maintenance (if applicable)
If your system includes battery storage:
- Keep batteries clean and dry.
- Check fluid levels in flooded lead-acid batteries and top up with distilled water if necessary.
- Ensure proper ventilation in the battery storage area.
- Monitor battery temperature and performance regularly.
7. Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintain detailed records of your system:
- Keep all manuals, warranties, and installation documentation in a safe place.
- Document all maintenance activities, including dates and actions taken.
- Record any issues encountered and how they were resolved.
- Save all receipts for parts or services related to your solar system for tax and warranty purposes.
8. Seasonal Considerations
Adjust your maintenance routine based on the seasons:
- Spring: Perform a thorough cleaning after winter and check for any damage from winter weather.
- Summer: Monitor for overheating issues and ensure proper ventilation.
- Fall: Clear fallen leaves and prepare the system for winter.
- Winter: Remove snow accumulation (if safe to do so) and check for ice damage.
9. Professional Inspections
Even with DIY maintenance, it’s wise to have a professional inspection periodically:
- Schedule a professional inspection every 2-3 years.
- Have a licensed electrician check all electrical components annually.
- Consider thermal imaging inspections to detect hot spots or other hidden issues.
10. Staying Informed
Keep yourself updated on solar technology and maintenance best practices:
- Join online forums or local solar enthusiast groups.
- Attend workshops or webinars on solar panel maintenance.
- Subscribe to industry newsletters for the latest information and tips.
By diligently following these maintenance responsibilities, you can ensure that your DIY solar power system operates efficiently for many years to come. Remember, while the initial investment in a DIY system might be lower, the ongoing commitment to maintenance is crucial for realizing the full benefits of your solar investment.
As we’ve explored the maintenance and upkeep aspects of both commercial and DIY solar power systems, you now have a comprehensive understanding of what’s involved in keeping your solar panels performing at their best. This knowledge will be invaluable as you move forward in making your final decision about which solar power option is right for you.
Making the Final Decision
Now that you’ve explored the various aspects of DIY and commercial solar power systems, it’s time to make the final decision. This crucial step will determine the future of your energy consumption and potentially impact your finances for years to come. Let’s dive into the key considerations that will help you make an informed choice.
Consulting with Experts
Before you make your final decision, it’s essential to consult with solar energy experts. Their knowledge and experience can provide valuable insights that you might have overlooked.
Types of Experts to Consult
- Solar Energy Consultants
- Certified Solar Installers
- Energy Auditors
- Financial Advisors
Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Personalized Advice: Experts can assess your specific situation and provide tailored recommendations.
- Up-to-date Information: They stay current with the latest solar technologies and regulations.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Professionals can help you understand the long-term financial implications of your decision.
- Technical Expertise: They can address complex technical questions about solar panel efficiency and system design.
Questions to Ask Experts
- What size system would be best for my energy needs?
- How will my roof’s condition and orientation affect solar panel installation?
- What are the local regulations and incentives for solar power in my area?
- How long will it take to recoup my investment through energy savings?
- What are the maintenance requirements for the system you recommend?
Remember, while expert advice is valuable, it’s important to gather opinions from multiple sources to get a well-rounded perspective.
Assessing Personal Circumstances
Your unique situation plays a crucial role in determining whether DIY or commercial solar power is right for you. Let’s examine some key factors you should consider:
Time and Skill Assessment
Ask yourself:
- Do you have the time to dedicate to a DIY solar project?
- Are you comfortable working with electrical systems and on rooftops?
- Can you navigate the permitting process and local regulations on your own?
If you answered “no” to any of these questions, a commercial solar installation might be more suitable for you.
Property Considerations
Evaluate your property:
- Roof Condition: Is your roof in good shape and able to support solar panels?
- Sun Exposure: Does your property receive adequate sunlight throughout the day?
- Available Space: Do you have enough unobstructed area for the number of panels you need?
Long-term Plans
Think about your future:
- How long do you plan to stay in your current home?
- Are you considering any major life changes that could affect your energy consumption?
- Do you foresee any changes in your financial situation that could impact your ability to maintain a solar system?
Energy Consumption Patterns
Analyze your energy usage:
- What’s your average monthly electricity consumption?
- Do you have any plans to increase or decrease your energy usage in the near future?
- Are there any energy-intensive appliances or activities you’re planning to add or remove?
Here’s a table to help you visualize how your energy consumption might affect your decision:
| Monthly Energy Usage (kWh) | Recommended System Size | DIY Feasibility | Commercial Recommendation |
| 0 – 500 | 3 – 4 kW | High | Optional |
| 501 – 1000 | 5 – 7 kW | Moderate | Recommended |
| 1001 – 1500 | 8 – 10 kW | Low | Highly Recommended |
| 1501+ | 11+ kW | Very Low | Essential |
Weighing Pros and Cons
Now that you’ve gathered information and assessed your personal circumstances, it’s time to weigh the pros and cons of DIY and commercial solar power installations. This step is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with your needs and goals.
DIY Solar Power: Pros and Cons Revisited
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of choosing the DIY route:
Pros:
- Cost Savings: By eliminating labor costs, you can potentially save 10-30% on your solar installation.
- Personal Satisfaction: There’s a sense of accomplishment in building and maintaining your own system.
- Flexibility: You have control over the project timeline and can work at your own pace.
- Learning Experience: You’ll gain in-depth knowledge about solar technology and energy systems.
Cons:
- Time-Intensive: DIY installations can take weeks or even months to complete.
- Risk of Errors: Mistakes in installation can lead to system inefficiencies or safety hazards.
- Limited Warranty Options: Many manufacturers don’t offer warranties for DIY installations.
- Permit Challenges: Navigating local regulations and obtaining necessary permits can be complex.
Commercial Solar Power: Advantages and Disadvantages Revisited
Now, let’s review the pros and cons of opting for a professional commercial installation:
Pros:
- Professional Expertise: Installers have the knowledge and experience to optimize your system’s performance.
- Time-Efficient: Commercial installations are typically completed within a few days.
- Comprehensive Warranties: Many companies offer long-term warranties covering both equipment and installation.
- Financing Options: Professional installers often provide various financing solutions, including leases and power purchase agreements.
Cons:
- Higher Upfront Costs: Professional installations generally come with a higher price tag due to labor costs.
- Less Control: You have limited say in the specifics of the installation process.
- Dependence on Contractor: You’ll need to rely on the installer for maintenance and repairs.
- Potential for Overselling: Some companies may try to sell you a larger system than you actually need.
Decision Matrix
To help you visualize and compare your options, consider using a decision matrix like the one below. Rate each factor on a scale of 1-5, with 5 being the most favorable:
| Factor | DIY Solar | Commercial Solar |
| Cost | 5 | 3 |
| Time Investment | 2 | 5 |
| Quality Assurance | 3 | 5 |
| Warranty Coverage | 2 | 5 |
| Personal Satisfaction | 5 | 3 |
| Long-term Performance | 3 | 4 |
| Maintenance Ease | 2 | 4 |
| Resale Value | 3 | 4 |
| Total Score | 25 | 33 |
Remember, this is just an example. You should fill in your own scores based on your personal assessment of each factor’s importance to you.
Making the Final Call
As you make your final decision, consider these key points:
- Budget Alignment: Does your chosen option fit within your financial means and long-term financial goals?
- Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with the level of risk associated with your preferred option?
- Time Commitment: Can you realistically dedicate the time required for a DIY installation, or would a quicker commercial installation be more suitable?
- Technical Comfort: Do you have the skills and confidence to handle a DIY installation, or would you feel more secure with professional expertise?
- Long-term Outlook: Which option aligns better with your future plans and potential changes in energy needs?
- Environmental Impact: Consider which option might lead to a more efficient system and greater reduction in your carbon footprint.
- Resale Value: Think about how your choice might affect your home’s value if you plan to sell in the future.
- Local Regulations: Ensure your decision complies with local building codes and homeowners’ association rules, if applicable.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The right choice depends on your unique circumstances, priorities, and goals. Take your time to carefully consider all factors before making your decision.
If you’re still unsure, consider these options:
- Start Small: Begin with a small DIY system and expand later if you’re comfortable.
- Hybrid Approach: Install part of the system yourself and hire professionals for more complex components.
- Delay and Save: If neither option feels right now, consider waiting and saving up for your preferred choice.
No matter which path you choose, transitioning to solar power is a key step toward energy independence and sustainability. Just exploring solar options is already a positive move toward a greener future.
As you move forward, if you choose DIY, start researching equipment and planning your project. If you prefer a commercial installation, begin reaching out to solar companies for quotes. With careful planning, you’ll soon enjoy the benefits of solar power.
In the end, whether you choose DIY or commercial, solar power is a step toward a sustainable and cost-effective energy future. Take time to assess your options and consult professionals if needed.





